Symptoms of Acetylcholine Deficiency
- Constipation/gastroparesis
- Memory problems
- Difficulty with word recall when speaking
- Learning difficulties
- Dry mouth
- Dry eyes
- Orthostatic hypotension
- Low muscle tone
- Depressed mood
- Fast heart rate
- Chronic inflammation
- Emotional instability
It's possible that the decline in acetylcholine levels in AD and dementia are due to a deficiency in the precursors needed to make it. So, let's talk about how acetylcholine is made next.
Acetylcholine synthesis
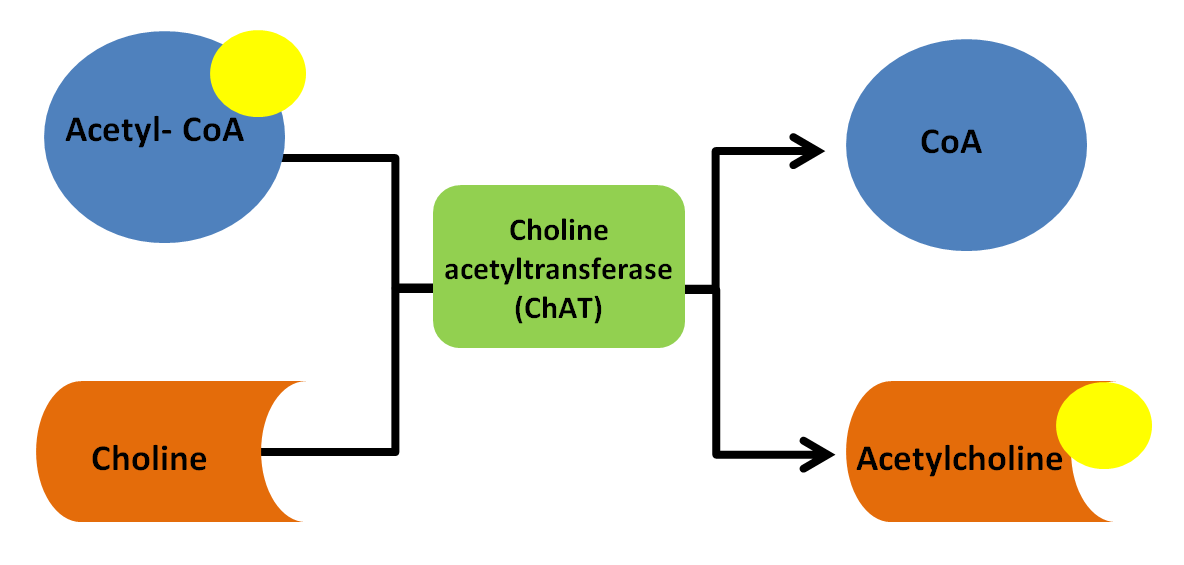
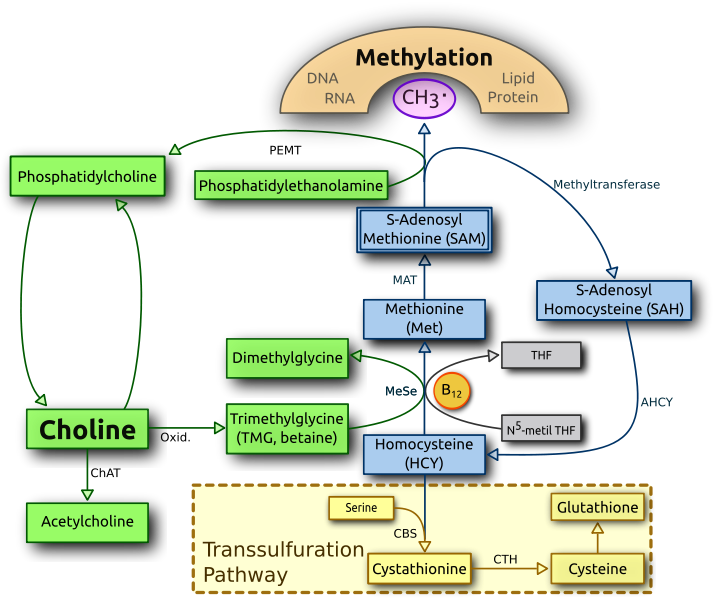
The enzyme that cleaves the acetyl group from acetyl CoA and attaches it to choline is choline acetyltransferase (ChAT) as seen in image 3.
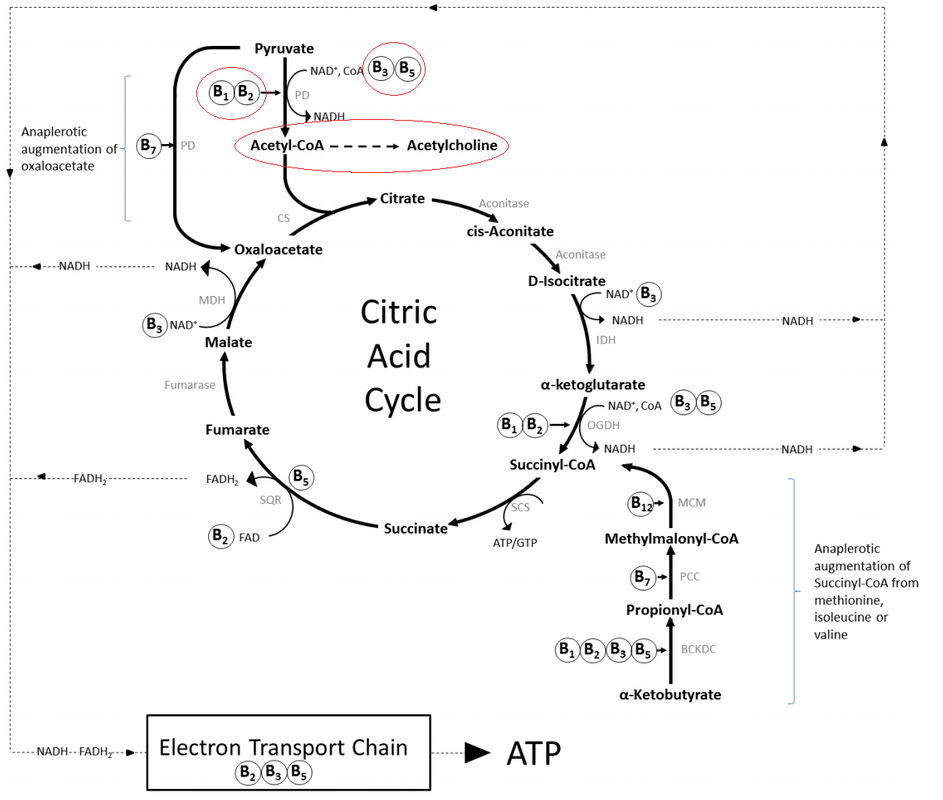
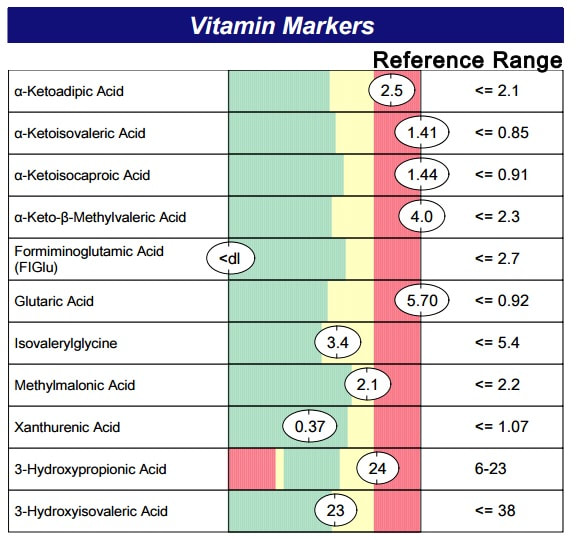
Deficiencies in these B vitamin cofactors is most often due to gastrointestinal malabsorption. Yeast overgrowth is a common cause of malabsorpton, especially of B vitamins. The best testing to determine a need for these B vitamins is organic acid testing. Results like the ones seen in image 5, for example, indicate a significant deficiency in B1, B2, B3 and B5. These are results for a child who has Down syndrome and is likely also deficient in ACh due to her B vitamin deficiencies, not her extra chromosome. The deficiencies in this child were due to small intestinal bacterial and fungal/candida overgrowth. Addressing these deficiencies along with the root cause of malabsorption is key to optimizing ACh synthesis.
Foods highest in choline include eggs (yolks) and meat, so vegans and vegetarians are at risk for being low in choline. Supplementation is possible by taking lecithin sourced from soy or sunflower. Lecithin is rich in phosphatidylcholine (PC), which is a precursor to choline. Citicoline and CDP-choline are other forms of choline that have been shown to enhance memory and cogntion. (Gareri, 2015; Fioravanti, 2006) Choline bitartrate should be avoided. It's the most commonly used form because it's the cheapest. It also is the least reliable form for impacting brain levels of choline (Lippelt, 2016) I prefer PC over other sources of choline because the production of PC is the second largest draw on methylation than all other process that require methylation combined. (Bertolo, 2013) Image 5 shows the production of PC from phosphatidylethanolamine via PEMT (phosphatidylethanolamine N-methyltransferase), a process that occurs in the liver. Because cell membranes consist largely of PC the body is required to make it often to keep up with cellular repair and growth. By supplying PC as a supplement this eases up on methylation and allows more methyl groups to be used for other methylation dependent processes.
As well, supplementing with PC has been shown to increase acetylcholine synthesis. Dr. Steven Heizel from the Department of Nutrition, School of Public Health and School of Medicine at the University of North Carolina stated, "Acetylcholine synthesis can be influenced by the availability of choline...its manipulation by changing the diet is likely to be a powerful tool for improving human performance.". (Heizel, 2006)
Genetic variations in mothers can alter choline requirements as well. Specifically variations in PEMT and MTHFR1 genes can alter endogenous synthesis of choline. Maternal dietary choline intake can influence global gene methylation and ultimately gene expression in the unborn child. (Bennett, 2016). Because not all mothers know their PEMT or MTHFR1 gene status supplementing with choline during pregnancy at approximately 980 mg per day, as was done in the study above, may help to ensure adequate levels are available for proper infant brain development. In addition, vegans are at high risk for being choline deficient and should definitely consider supplementing. Vegetarians who eat eggs daily are less likely to be deficient. One egg contains about 150 mg of choline.
Natural cholinesterase inhibitors
| Bacopa monnieri (also known as brahmi, water hyssop, and Herpestis monniera) is one of my favorite nootropic herbs. It has the lowest chance of creating side effects over other forms of cholinesterase inhibitors. "Emerging research demonstrates several mechanisms of action—acetylcholinesterase inhibition, choline acetyltransferase activation, b-amyloid reduction, increased cerebral blood flow, and monoamine potentiation." (Aguiar and Borowski, 2013) One side effect that is possible with Bacopa is loose stools. This is likely due to increased levels of ACh. The dose can be reduced if this occurs. However, Kumar, et al stated "Bacopa in syrup form, equivalent to 1 gm dried Bacopa daily, for three months in 40 school children aged 6–8 years, showed improvement in immediate memory, perception, and reaction performance without any side effects." (Kumar, 2016). |
Gohil et al report "CA has no known toxicity in recommended doses. Side effects are rare but may include skin allergy and burning sensations (with external use), headache, stomach upset, nausea, dizziness, and extreme drowsiness which tend to occur with high doses of the herb." (Gohil, 2010)
Both Bacopa and Gotu Kola were used in a formula that was tested in children with ADHD. It was not only shown to be effective but "No serious adverse events were reported, and the rate of even mild adverse events among CHP-treated patients was actually less than that of placebo. (Katz, 2010). (CHP is compound herbal preparation.)
Potential side effects include nausea, diarrhea, vomiting, sweating, blurred vision, slurred speech, restlessness, loss of appetite, contraction and twitching of muscle fibers, cramping, increased saliva and urine, inability to control urination, high blood pressure, and slowed heart rate. (WebMD)
For these reasons, along with focusing on addressing root cause, I don't typically recommend using Huperzine A in my patients.
Down Syndrome
They moved on in 2017 with researching actual maternal choline supplementation (MCS) in the Ts65Dn mouse model. They were able to state, "These results support the lifelong attentional benefits of MCS for Ts65Dn and 2N offspring and have profound implications for translation to human DS and pathology attenuation in AD." (Strupp, 2017)
In 1986 a report of supplementing phosphatidylcholine in a 2.5 year old child with Down syndrome was published. They reported no other supplements given. After 7 months "The child showed a definitive increase in speech and language skills as well as general motor skills which exceeded same aged Down Syndrome peers experiencing like training programs." (Cantor, 1986)
| Thiamine supplementation at 50 mg given three times per day has also been shown to improve speech, mood, energy and cognition in adults with Down syndrome. (Reading, 1979) The mechanism behind these changes are likely due to an increase in ACh as well as the many other benefits thiamine supplementation provides. |
Steps to optimize ACh synthesis for your child
- Review signs and symptoms of ACh deficiency with their physician. Determine if need to support ACh synthesis exists.
- Test for B vitamin deficiencies using organic acid testing. Clues to B vitamin deficiencies can be seen in routine labs as elevated fasting blood sugar, low ferritin, elevated MCV, among others.
- Supplement with phosphatidylcholine, especially when eggs and meat are low in the diet
- Supplement with phosphatidylcholine if pregnant or breastfeeding, especially if following a vegan or vegetarian diet
- Supplement with appropriate levels of B vitamins specific for your child as indicated by test results
- Address underlying root cause for malabsorption of B vitamins. Organic acid testing and stool analysis can detect gastrointestinal issues contributing to malabsorption.



 RSS Feed
RSS Feed