|
Healthy brain function relies on a variety of biochemical factors including neurotransmitters, neurotrophic factors, neurohormones, antioxidants, omega-3 fatty acids, glucose, B-vitamins, minerals and phospholipids.
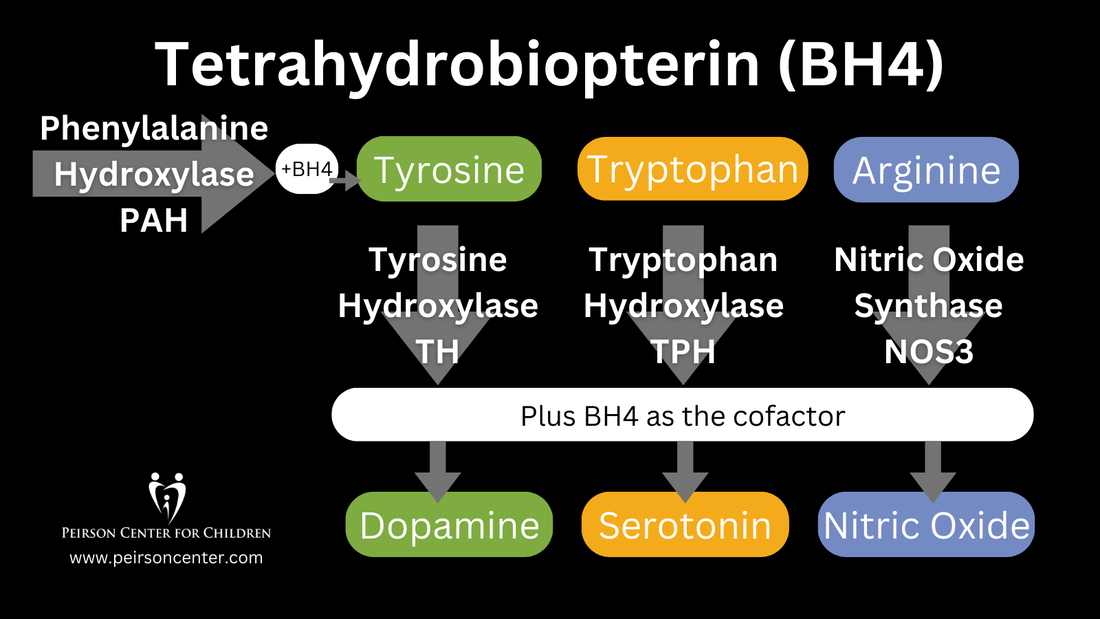
Tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4) is one of many important factors that impact neurotransmitters in the brain and nervous system. It's a vital cofactor in the synthesis of several neurotransmitters and is crucial for multiple metabolic pathways in the body. |
This article will explore the role of BH4 in neurotransmitter synthesis, its impact on dopamine, serotonin, and nitric oxide, as well as the influence of folinic acid and methylfolate on the BH4 cycle. Additionally, signs and symptoms of low BH4 levels will be discussed.
BH4 plays a critical role in the synthesis of dopamine, serotonin, and nitric oxide, neurotransmitters essential for healthy neurological function. In the synthesis of dopamine, BH4 acts as a cofactor for the enzyme tyrosine hydroxylase, which converts tyrosine to L-DOPA, a precursor of dopamine. Without adequate BH4 levels, dopamine synthesis is impaired, leading to disruptions in neurological function. Similarly, BH4 is essential for the synthesis of serotonin, as it is a cofactor for tryptophan hydroxylase, the enzyme responsible for converting tryptophan to 5-hydroxytryptophan (5-HTP), a precursor of serotonin. Furthermore, BH4 is involved in the synthesis of nitric oxide (NO) as a cofactor for nitric oxide synthase (NOS). NO is a signaling molecule involved in various physiological processes, including vasodilation and neurotransmission.
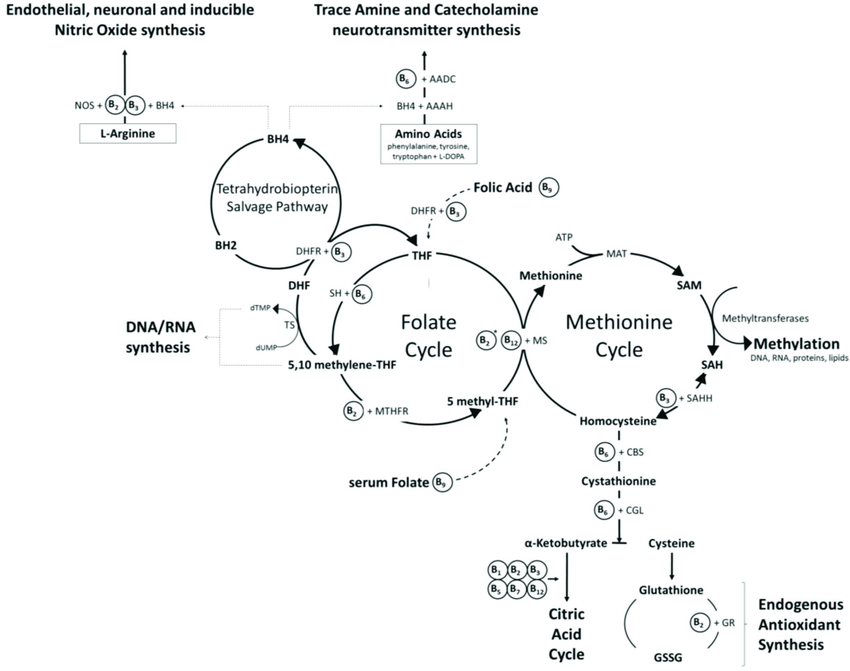
Folinic acid and methylfolate play crucial roles in the BH4 cycle by influencing the availability of BH4. Folinic acid, also known as 5-formyltetrahydrofolate, is a precursor to BH4 and is involved in its synthesis. Methylfolate, the active form of folate, is necessary for the conversion of homocysteine to methionine in the methionine cycle. Methionine, in turn, is essential for the regeneration of BH4 from its oxidized form, dihydrobiopterin (BH2). Therefore, adequate levels of folinic acid and methylfolate are necessary for the proper functioning of the BH4 cycle and the synthesis of neurotransmitters.
|
Low levels of BH4 can lead to a range of signs and symptoms, including neurological and psychiatric manifestations. Neurological symptoms may include developmental delay, movement disorders, such as dystonia or tremors, and seizures. Psychiatric symptoms associated with low BH4 levels may include mood disturbances, such as depression or anxiety, as well as cognitive impairments. Low levels of BH4 resulting in low dopamine can even impact speech resulting in ataxia and stutter. Additionally, individuals with low BH4 levels may experience cardiovascular dysfunction due to impaired nitric oxide synthesis, leading to hypertension or vascular complications.
|
|
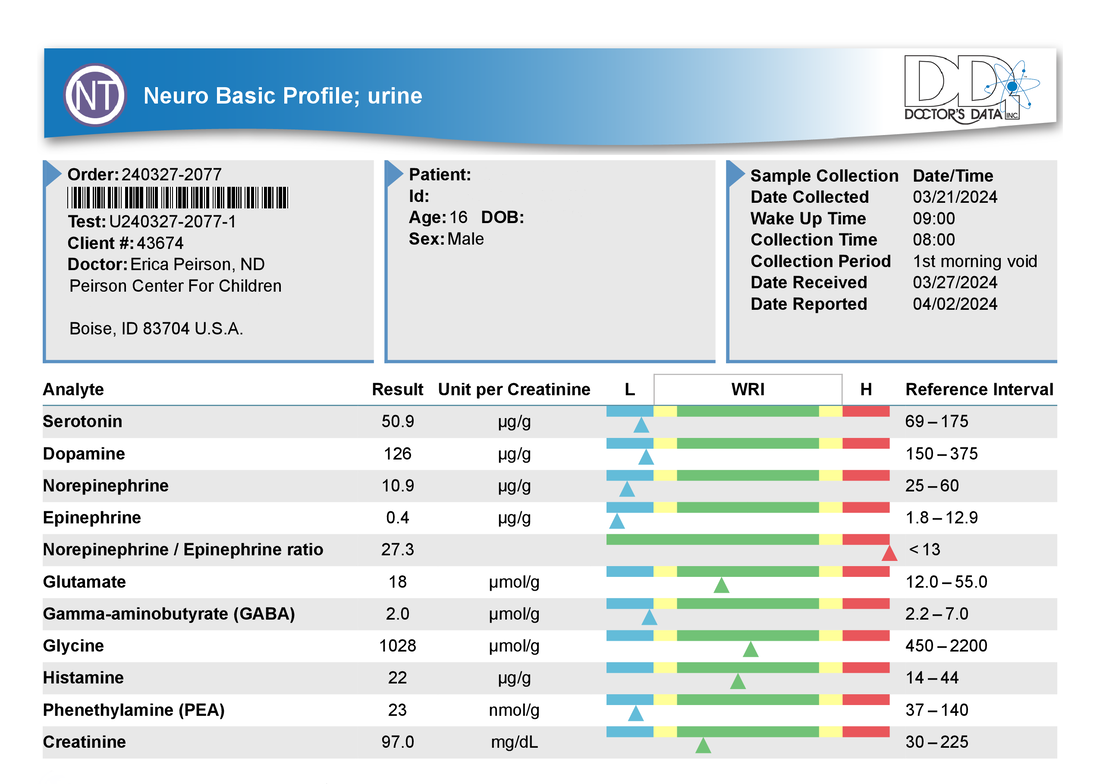
A commercial test for assessing a BH4 level in the body is not commercially available at this time. However, nitric oxide levels can be tested safely and easily in saliva using humanN test strips seen here. As well a urine neurotransmitter test like the NeuroBasic Profile can be done through Doctor's Data that includes dopamine and serotinin levels. A sample report of this test can be seen here from a patient who has a stutter, which has been linked to low dopamine levels. (Alm 2021)
|
The role this process plays in children with Down syndrome is important to note as well. BH4 levels have been found to be low in children with Down syndrome. (Aziz 1982)
In conclusion, tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4) is a critical cofactor involved in the synthesis of dopamine, serotonin, and nitric oxide, neurotransmitters essential for neurological and physiological function. Folinic acid and methylfolate influence the BH4 cycle and are necessary for BH4 synthesis and regeneration. Low BH4 levels can result in a range of neurological, psychiatric, and cardiovascular symptoms. Understanding the role of BH4 and its associated pathways is crucial for optimizing brain health. Working with a nutritionally trained physician who can recommend the right dose of folinic acid and/or methylfolate when warranted can improve BH4 production and overall brain health.
If you're interested in reading more about this I highly recommend: Tetrahydrobioterin (BH4) Pathway: From Metabolism to Neuropsychiatry
As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases.




 RSS Feed
RSS Feed